The Pirates Own Book, by Charles Ellms
HISTORY OF THE ADVENTURES,
CAPTURE AND EXECUTION OF THE SPANISH PIRATES.
In the Autumn of 1832, there was anchored in the "Man of War Grounds," off the Havana, a clipper-built vessel of the fairest proportions; she had great length and breadth of beam, furnishing stability to bear a large surface of sail, and great depth to take hold of the water and prevent drifting; long, low in the waist, with lofty raking masts, which tapered away till they were almost too fine to be distinguished, the beautiful arrowy sharpness of her bow, and the fineness of her gradually receding quarters, showed a model capable of the greatest speed in sailing. Her low sides were painted black, with one small, narrow ribband of white. Her raking masts were clean scraped, her ropes were hauled taught, and in every point she wore the appearance of being under the control of seamanship and strict discipline. Upon going on board, one would be struck with surprise at the deception relative to the tonnage of the schooner, when viewed at a distance. Instead of a small vessel of about ninety tons, we discover that she is upwards of two hundred; that her breadth of beam is enormous; and that those spars which appeared so light and elegant, are of unexpected dimensions. In the centre of the vessel, between the fore and main masts, there is a long brass thirty-two pounder, fixed upon a carriage revolving in a circle, and so arranged that in bad weather it can be lowered down and housed; while on each side of the deck were mounted guns of smaller calibre.
This vessel was fashioned, at the will of avarice, for the aid of cruelty and injustice; it was an African slaver--the schooner Panda. She was commanded by Don Pedro Gilbert, a native of Catalonia, in Spain, and son of a grandee; a man thirty-six years of age, and exceeding handsome, having a round face, pearly teeth, round forehead, and full black eyes, with beautiful raven hair, and a great favorite with the ladies. He united great energy, coolness and decision, with superior knowledge in mercantile transactions, and the Guinea trade; having made several voyages after slaves. The mate and owner of the Panda was Don Bernardo De Soto, a native of Corunna, Spain, and son, of Isidore De Soto, manager of the royal revenue in said city; he was now twenty-five years of age, and from the time he was fourteen had cultivated the art of navigation, and at the age of twenty-two had obtained the degree of captain in the India service. After a regular examination the correspondent diploma was awarded him. He was married to Donna Petrona Pereyra, daughter of Don Benito Pereyra, a merchant of Corunna. She was at this time just fifteen, and ripening into that slight fullness of form, and roundness of limb, which in that climate mark the early passing from girl into woman. Her complexion was the dark olive tinge of Spain; her eyes jet black, large and lustrous. She had great sweetness of disposition and ingenuousness.
To the strictest discipline De Soto united the practical knowledge of a thorough seaman. But "the master spirit of the whole," was Francisco Ruiz, the carpenter of the Panda. This individual was of the middle size, but muscular, with a short neck. His hair was black and abundant, and projected from his forehead, so that he appeared to look out from under it, like a bonnet. His eyes were dark chestnut, but always restless; his features were well defined; his eye-lashes, jet black. He was familiar with all the out-of-the-way places of the Havana, and entered into any of the dark abodes without ceremony. From report his had been a wild and lawless career. The crew were chiefly Spaniards, with a few Portuguese, South Americans, and half castes. The cook was a young Guinea negro, with a pleasant countenance, and good humored, with a sleek glossy skin, and tatooed on the face; and although entered in the schooner's books as free, yet was a slave. In all there were about forty men. Her cargo was an assorted one, consisting in part of barrels of rum, and gunpowder, muskets, cloth, and numerous articles, with which to purchase slaves.
The Panda sailed from the Havana on the night of the 20th of August; and upon passing the Moro Castle, she was hailed, and asked, "where bound?" She replied, St. Thomas. The schooner now steered through the Bahama channel, on the usual route towards the coast of Guinea; a man was constantly kept at the mast head, on the lookout; they spoke a corvette, and on the morning of the 20th Sept., before light, and during the second mate's watch, a brig was discovered heading to the southward. Capt. Gilbert was asleep at the time, but got up shortly after she was seen, and ordered the Panda to go about and stand for the brig. A consultation was held between the captain, mate and carpenter, when the latter proposed to board her, and if she had any specie to rob her, confine the men below, and burn her. This proposition was instantly acceded to, and a musket was fired to make her heave to.
This vessel was the American brig Mexican, Capt. Butman. She had left the pleasant harbor of Salem, Mass., on the last Wednesday of August, and was quietly pursuing her voyage towards Rio Janeiro. Nothing remarkable had happened on board, says Captain B., until half past two o'clock, in the morning of September 20th, in lat. 38, 0, N., lon. 24, 30, W. The attention of the watch on deck was forcibly arrested by the appearance of a vessel which passed across our stern about half a mile from us. At 4 A.M. saw her again passing across our bow, so near that we could perceive that it was a schooner with a fore top sail and top gallant sail. As it was somewhat dark she was soon out of sight. At daylight saw her about five miles off the weather quarter standing on the wind on the same tack we were on, the wind was light at SSW and we were standing about S.E. At 8 A.M. she was about two miles right to windward of us; could perceive a large number of men upon her deck, and one man on the fore top gallant yard looking out; was very suspicious of her, but knew not how to avoid her. Soon after saw a brig on our weather bow steering to the N.E. By this time the schooner was about three miles from us and four points forward of the beam. Expecting that she would keep on for the brig ahead of us, we tacked to the westward, keeping a little off from the wind to make good way through the water, to get clear of her if possible. She kept on to the eastward about ten or fifteen minutes after we had tacked, then wore round, set square sail, steering directly for us, came down upon us very fast, and was soon within gun shot of us, fired a gun and hoisted patriot colors and backed main topsail. She ran along to windward of us, hailed us to know where we were from, where bound, &c. then ordered me to come on board in my boat. Seeing that she was too powerful for us to resist, I accordingly went, and soon as I got along-side of the schooner, five ruffians instantly jumped into my boat, each of them being armed with a large knife, and told me to go on board the brig again; when they got on board they insisted that we had got money, and drew their knives, threatening us with instant death and demanding to know where it was. As soon as they found out where it was they obliged my crew to get it up out of the run upon deck, beating and threatening them at the same time because they did not do it quicker. When they had got it all upon deck, and hailed the schooner, they got out their launch and came and took it on board the schooner, viz: ten boxes containing twenty thousand dollars; then returned to the brig again, drove all the crew into the forecastle, ransacked the cabin, overhauling all the chests, trunks, &c. and rifled my pockets, taking my watch, and three doubloons which I had previously put there for safety; robbed the mate of his watch and two hundred dollars in specie, still insisting that there was more money in the hold. Being answered in the negative, they beat me severely over the back, said they knew that there was more, that they should search for it, and if they found any they would cut all our throats. They continued searching about in every part of the vessel for some time longer, but not finding any more specie, they took two coils of rigging, a side of leather, and some other articles, and went on board the schooner, probably to consult what to do with us; for, in eight or ten minutes they came back, apparently in great haste, shut us all below, fastened up the companion way, fore-scuttle and after hatchway, stove our compasses to pieces in the binnacles, cut away tiller-ropes, halliards, braces, and most of our running rigging, cut our sails to pieces badly; took a tub of tarred rope-yarn and what combustibles they could find about deck, put them in the caboose house and set them on fire; then left us, taking with them our boat and colors. When they got alongside of the schooner they scuttled our boat, took in their own, and made sail, steering to the eastward.
As soon as they left us, we got up out of the cabin scuttle, which they had neglected to secure, and extinguished the fire, which if it had been left a few minutes, would have caught the mainsail and set our masts on fire. Soon after we saw a ship to leeward of us steering to the S.E. the schooner being in pursuit of her did not overtake her whilst she was in sight of us.
It was doubtless their intention to burn us up altogether, but seeing the ship, and being eager for more plunder they did not stop fully to accomplish their design. She was a low strait schooner of about one hundred and fifty tons, painted black with a narrow white streak, a large head with the horn of plenty painted white, large maintopmast but no yards or sail on it. Mast raked very much, mainsail very square at the head, sails made with split cloth and all new; had two long brass twelve pounders and a large gun on a pivot amidships, and about seventy men, who appeared to be chiefly Spaniards and mulattoes.

Pirates robbing the brig Mexican of Salem, Mass.
The object of the voyage being frustrated by the loss of the specie, nothing now remained but for the Mexican to make the best of her way back to Salem, which she reached in safety. The government of the United States struck with the audacity of this piracy, despatched a cruiser in pursuit of them. After a fruitless voyage in which every exertion was made, and many places visited on the coast of Africa, where it was supposed the rascals might be lurking, the chase was abandoned as hopeless, no clue being found to their "whereabouts."
The Panda after robbing the Mexican, pursued her course across the Atlantic, and made Cape Monte; from this she coasted south, and after passing Cape Palmas entered the Gulf of Guinea, and steered for Cape Lopez which she reached in the first part of November. Cape Lopez de Gonzalves, in lat. 0° 36' 2" south, long. 80° 40' 4" east, is so called from its first discoverer. It is covered with wood but low and swampy, as is also the neighboring country. The extensive bay formed by this cape is fourteen miles in depth, and has several small creeks and rivers running into it. The largest is the river Nazareth on the left point of which is situated King Gula's town the only assemblage of huts in the bay. Here the cargo of the Panda was unloaded, the greater part was entrusted to the king, and with the rest Capt. Gilbert opened a factory and commenced buying various articles of commerce, as tortoise shell, gum, ivory, palm oil, fine straw carpeting, and slaves. After remaining here a short time the crew became sickly and Capt. Gilbert sailed for Prince's Island to recover the health of his crew. Whilst at Prince's Island news arrived of the robbery of the Mexican. And the pirate left with the utmost precipitation for Cape Lopez, and the better to evade pursuit, a pilot was procured; and the vessel carried several miles up the river Nazareth. Soon after the Panda left Prince's Island, the British brig of war, Curlew, Capt. Trotter arrived, and from the description given of the vessel then said to be lying in the Nazareth, Capt. Trotter knew she must be the one, that robbed the Mexican; and he instantly sailed in pursuit. On nearing the coast, she was discovered lying up the river; three boats containing forty men and commanded by Capt. Trotter, started up the river with the sea breeze and flood tide, and colors flying to take the desperadoes; the boats kept in near the shore until rounding a point they were seen from the Panda. The pirates immediately took to their boats, except Francisco Ruiz who seizing a fire brand from the camboose went into the magazine and set some combustibles on fire with the laudable purpose of blowing up the assailants, and then paddled ashore in a canoe. Capt. Trotter chased them with his boats, but could not come up with them, and then boarded the schooner which he found on fire. The first thing he did was to put out the fire which was in the magazine, below the cabin floor; here was found a quantity of cotton and brimstone burning and a slow match ignited and communicating with the magazine, which contained sixteen casks of powder.
The Panda was now warped out of the river and anchored off the negro town of Cape Lopez. Negociations were now entered into for the surrender of the pirates. An officer was accordingly sent on shore to have an interview with the king. He was met on the beach by an ebony chief calling himself duke. "We followed the duke through the extensive and straggling place, frequently buried up to the ankles in sand, from which the vegetation was worn by the constant passing and repassing of the inhabitants. We arrived at a large folding door placed in a high bamboo and palm tree fence, which inclosed the king's establishment, ornamented on our right by two old honeycombed guns, which, although dismounted, were probably, according to the practice of the coast, occasionally fired to attract the attention of passing vessels, and to imply that slaves were to be procured. On the left of the enclosure was a shed, with a large ship's bell suspended beneath, serving as an alarum bell in case of danger, while the remainder was occupied with neatly built huts, inhabited by the numerous wives of the king.
"We sent in to notify him of our arrival; he sent word out that we might remain outside until it suited his convenience. But as such an arrangement did not suit ours, we immediately entered, and found sitting at a table the king. He was a tall, muscular, ugly looking negro, about fifty years of age. We explained the object of our visit, which was to demand the surrender of the white men, who were now concealed in the town, and for permission to pass up the river in pursuit of those who had gone up that way. He now expressed the most violent indignation at our presumption in demanding the pirates, and the interview was broken off by his refusing to deliver up a single man."
We will now return to the pirates. While at Prince's Island, Capt. Gilbert bought a magnificent dressing case worth nearly a thousand dollars and a patent lever watch, and a quantity of tobacco, and provisions, and two valuable cloth coats, some Guinea cloth and black and green paint. The paint, cloth and coats were intended as presents for the African king at Cape Lopez. These articles were all bought with the money taken from the Mexican. After arriving at the Nazareth, $4000 were taken from the trunk, and buried in the yard of a negro prince. Four of the pirates then went to Cape Lopez for $11,000, which had been buried there. Boyga, Castillo, Guzman, and the "State's Evidence," Ferez, were the ones who went. Ferez took the bags out, and the others counted the money; great haste was made as the musquitoes were biting intolerably. $5000 were buried for the captain in canvas bags about two feet deep, part of the money was carried to Nazareth, and from there carried into the mountains and there buried. A consultation was held by Capt. Gilbert, De Soto, and Ruiz, and the latter said, if the money was not divided, "there would be the devil to pay." The money was now divided in a dark room and a lantern used; Capt. Gilbert sat on the floor with the money at his side. He gave the mate about $3000, and the other officers $1000, each; and the crew from $300 to $500, each. The third mate having fled, the captain sent him $1000, and Ruiz carried it to him. When the money was first taken from the Mexican, it was spread out on the companion way and examined to see if there was any gold amongst it; and then put into bags made of dark coarse linen; the boxes were then thrown overboard. After the division of the money the pirates secreted themselves in the woods behind Cape Lopez. Perez and four others procured a boat, and started for Fernando Po; they put their money in the bottom of the boat for ballast, but was thrown overboard, near a rock and afterwards recovered by divers; this was done to prevent detection. The captain, mate, and carpenter had a conversation respecting the attempt of the latter, to blow her up, who could not account for the circumstance, that an explosion had not taken place; they told him he ought to have burst a barrel of powder over the deck and down the stairs to the magazine, loaded a gun, tied a fish line to the lock and pulled it when he came off in the canoe.

View of the Negro village on the river Nazareth, and the Panda at anchor.
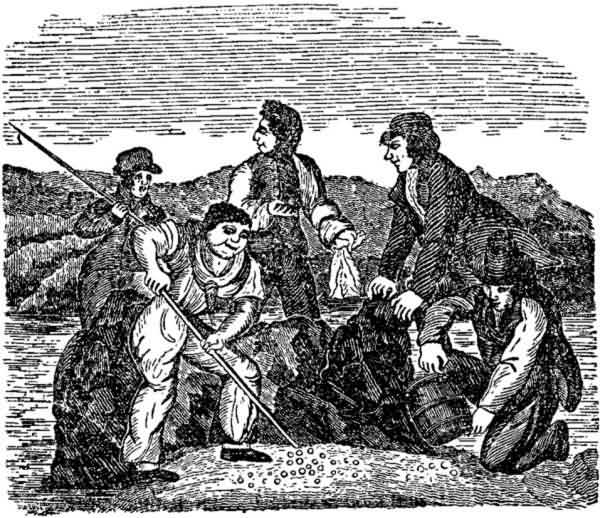
The Panda being manned by Capt. Trotter and an English crew,
commenced firing on the town of Cape Lopez, but after firing
several shots, a spark communicated with the magazine and she
blew up. Several men were killed, and Captain Trotter and the
others thrown into the water, when he was made prisoner with
several of his crew, by the King, and it required considerable
negociations to get them free.

Burying the money on the beach at Cape Lopez.
The pirates having gone up the river, an expedition was now equipped to take them if possible. The long-boat and pinnace were instantly armed, and victualled for several weeks, a brass gun was mounted on the bows of each, and awnings fixed up to protect the crew from the extreme heat of the sun by day, and the heavy dews at nightfall. As the sea-breeze and the flood-tide set in, the boats again started and proceeded up the river. It was ascertained the war-canoes were beyond where the Panda was first taken; for fear of an ambuscade great caution was observed in proceeding. "As we approached a point, a single native was observed standing near a hut erected near the river, who, as we approached, beckoned, and called for us to land. We endeavored to do so, but fortunately the water was too shallow to approach near enough.
"We had hardly steered about for the channel, when the man suddenly rushed into the bushes and disappeared. We got into the channel, and continued some time in deep water, but this suddenly shoaled, and the boats grounded near a mangrove, just as we came in sight of a village. Our crew jumped out, and commenced tracking the boat over the sand, and while thus employed, I observed by means of my glass, a crowd of natives, and some of the pirates running down the other side of a low point, apparently with the intention of giving us battle, as they were all armed with spears and muskets."
The men had just succeeded in drawing the boats into deep water, when a great number of canoes were observed coming round the point, and at the same instant another large party running down to launch; some more on the beach, when they joined those already afloat, in all made above twenty-eight canoes, and about one hundred and fifty men. Having collected all their forces, with loud whooping and encouraging shouts to one another, they led towards us with great celerity.
We prepared instantly for battle; the awnings were got down to allow room to use the cutlasses and to load the muskets. The brass guns were loaded with grape shot. They now approached uttering terrific yells, and paddling with all speed. On board the canoes the pirates were loading the guns and encouraging the natives. Bernardo de Soto and Francisco Ruiz were conspicuous, in manoeuvring the negro boats for battle, and commenced a straggling fire upon the English boats. In them all was still, each man had a cutlass by his side, and a loaded musket in his hand. On arriving within pistol-shot a well directed fire was poured into them, seconded by a discharge of the three pounders; many of the balls took effect, and two of the canoes were sunk. A brisk fire was kept up on both sides; a great number of the negroes were killed, and a few of the pirates; the English loss was small. The negroes now became panic-struck, and some paddled towards the shore, others jumped overboard and swam; the sharks caught several. Captain Gilbert and De Soto were now caught, together with five of the crew; Ruiz and the rest escaped to a village, some ways inland, and with the aid of a telescope it was perceived the negroes were rapidly gathering to renew the combat, urged on by Ruiz and the other pirates; after dislodging them from this village, negociations were entered into by the king of Cape Lopez, who surrendered Ruiz and several men to Captain Trotter. They were carried in the brig Curlew to Fernando Po, and after an examination, were put in irons and conveyed to England, and there put on board the British gun-brig Savage, and arrived in the harbor of Salem on the 26th August, 1834. Her commander, Lieut. Loney, waited upon the authorities of Salem, and after the usual formalities, surrendered the prisoners into their hands--stating that the British Government waived their right to try and punish the prisoners, in favor of the United States, against whom the principal offence had been committed. The pirates were landed at Crowningshield wharf, and taken from thence in carriages to the Town hall; twelve of them, handcuffed in pairs, took their places at the bar. They were all young and middle-aged, the oldest was not over forty. Physiognomically, they were not uncommonly ill looking, in general, although there were exceptions, and they were all clean and wholesome in their appearance. They were now removed to Boston and confined in prison, where one of them, named Manuel Delgarno cut his throat with a piece of glass, thus verifying the old proverb, that those born to be hung, will never be drown'd!
On the 11th of November, Don Pedro Gilbert, Captain,
Don Bernardo de Soto, Mate, Francisco Ruiz,
Carpenter, Nicola Costa, Cabin-boy, aged 15,
Antonio Ferrer, Cook, and Manuel Boyga, Domingo de Guzman,
an Indian, Juan Antonio Portana, Manuel Castillo, Angel
Garcia, Jose Velasquez, and Juan Montenegro, alias Jose
Basilio de Castro, were arraigned before the Circuit Court of the
United States, charged with the crime of Piracy. Joseph Perez
appeared as State's evidence, and two Portuguese sailors
who were shipped on board the Panda at Prince's Island, as
witnesses. After a jury was empannelled, Mr. Dunlap, the District
Attorney, rose and said--"This is a solemn, and also an unusual
scene. Here are twelve men, strangers to our country and to our
language, indicted for a heinous offence, and now before you for
life or death. They are indicted for a daring crime, and a
flagrant violation of the laws, not only of this, but of every
other civilized people." He then gave an outline of the
commission of the robbery of the Mexican. Numerous witnesses were
examined, amongst whom were the captain, mate, and several seamen
of the Mexican, who recognized several of the pirates as being
the individuals who maltreated them, and took the specie. When
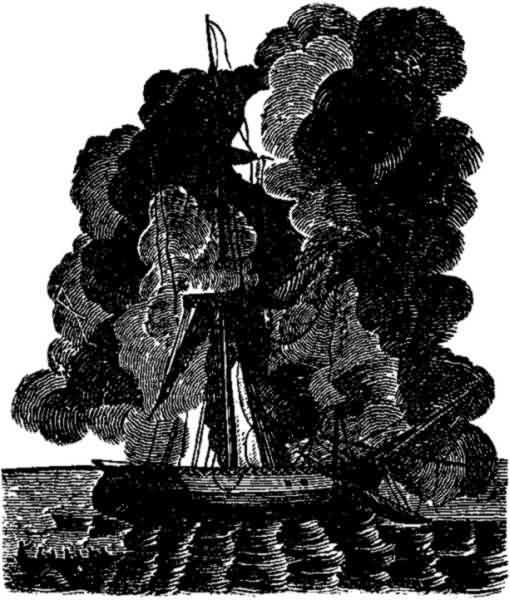
Thomas Fuller, one of the crew of the Mexican was called upon to
identify Ruiz, he went up to him and struck him a violent blow on
the shoulder. Ruiz immediately started up, and with violent
gesticulations protested against such conduct, and was joined by
his companions. The Court reprimanded the witness severely. The
trial occupied fourteen days. The counsel for the
prisoners were David L. Child, Esq., and George Hillard, Esq.,
who defended them with great ability. Mr. Child brought to the
cause his untiring zeal, his various and profound learning; and
exhibited a labour, and desperation which showed that he
was fully conscious of the weight of the load--the dead lift--he
had undertaken to carry. Mr. Hillard concluded his argument, by
making an eloquent and affecting appeal to the jury in behalf of
the boy Costa and Antonio Ferrer, the cook, and alluded to the
circumstance of Bernardo de Soto having rescued the lives of 70
individuals on board the American ship Minerva, whilst on a
voyage from Philadelphia to Havana, when captain of the brig
Leon.

Explosion of the Panda.
If, gentlemen, said he, you deem with me, that the crew of the Panda, (supposing her to have robbed the Mexican,) were merely servants of the captain, you cannot convict them. But if you do not agree with me, then all that remains for me to do, is to address a few words to you in the way of mercy. It does not seem to me that the good of society requires the death of all these men, the sacrifice of such a hecatomb of human victims, or that the sword of the law should fall till it is clogged with massacre. Antonio Ferrer is plainly but a servant. He is set down as a free black in the ship's papers, but that is no proof that he is free. Were he a slave, he would in all probability be represented as free, and this for obvious reasons. He is in all probability a slave, and a native African, as the tattooing on his face proves beyond a doubt. At any rate, he is but a servant. Now will you make misfortune pay the penalty of guilt? Do not, I entreat you, lightly condemn this man to death. Do not throw him in to make up the dozen. The regard for human life is one of the most prominent proofs of a civilized state of society. The Sultan of Turkey may place women in sacks and throw them into the Bosphorus, without exciting more than an hour's additional conversation at Constantinople. But in our country it is different. You well remember the excitement produced by the abduction and death of a single individual; the convulsions which ensued, the effect of which will long be felt in our political institutions. You will ever find that the more a nation becomes civilized, the greater becomes the regard for human life. There is in the eye, the form, and heaven-directed countenance of man, something holy, that forbids he should be rudely touched.
The instinct of life is great. The light of the sun even in chains, is pleasant; and life, though supported but by the damp exhalations of a dungeon, is desirable. Often, too, we cling with added tenacity to life in proportion as we are deprived of all that makes existence to be coveted.
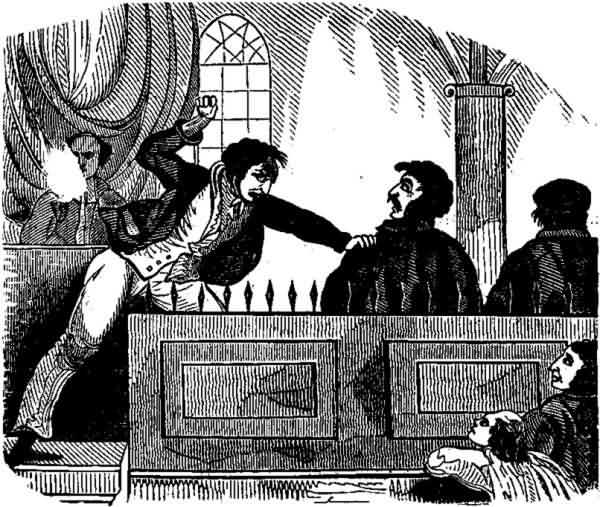

Thomas Fuller striking Ruiz in Court.
"The weariest and most loathed worldly life.
That age, ache, penury and
imprisonment
Can lay on Nature, is a
Paradise
To that we fear of
Death."
Death is a fearful thing. The mere mention of it sometimes blanches the cheek, and sends the fearful blood to the heart. It is a solemn thing to break into the "bloody house of life." Do not, because this man is but an African, imagine that his existence is valueless. He is no drift weed on the ocean of life. There are in his bosom the same social sympathies that animate our own. He has nerves to feel pain, and a heart to throb with human affections, even as you have. His life, to establish the law, or to further the ends of justice, is not required. Taken, it is to us of no value; given to him, it is above the price of rubies.
And Costa, the cabin boy, only fifteen years of age when this crime was committed--shall he die? Shall the sword fall upon his neck? Some of you are advanced in years--you may have children. Suppose the news had reached you, that your son was under trial for his life, in a foreign country--(and every cabin boy who leaves this port may be placed in the situation of this prisoner,)--suppose you were told that he had been executed, because his captain and officers had violated the laws of a distant land; what would be your feelings? I cannot tell, but I believe the feelings of all of you would be the same, and that you would exclaim, with the Hebrew, "My son! my son! would to God I had died for thee." This boy has a father; let the form of that father rise up before you, and plead in your hearts for his offspring. Perhaps he has a mother, and a home. Think of the lengthened shadow that must have been cast over that home by his absence. Think of his mother, during those hours of wretchedness, when she has felt hope darkening into disappointment, next into anxiety, and from anxiety into despair. How often may she have stretched forth her hands in supplication, and asked, even the winds of heaven, to bring her tidings of him who was away? Let the supplications of that mother touch your hearts, and shield their object from the law.
After a luminous charge by Judge Story, the jury retired to agree upon their verdict, and at 9 o'clock the next morning came in with their verdict.
Clerk. Gentlemen of the Jury, have you agreed upon your verdict?
Jury. We have.
Clerk. Who shall speak for you?
Jury. Our foreman.
The prisoners were then directed severally to rise as soon as called, and receive the verdict of the jury. The Captain, Pedro Gilbert, was the first named. He arose, raised his hand, and regarded the jury with a firm countenance and steady eye.
Clerk. Jurors look upon the prisoner; prisoner look upon the jurors. How say you, Gentlemen, is the prisoner at the bar, Pedro Gilbert, guilty or not guilty?
Foreman. GUILTY.
The same verdict was pronounced against De Soto (the mate) Ruiz, (the carpenter,) Boyga, Castillo, Garcia and Montenegro. But Costa, (the cabin-boy,) Ferrer (the negro,) Guzman, Portana, and Velasquez, were declared NOT GUILTY.
After having declared the verdict of the Jury, the Foreman read to the Court the following recommendation to mercy:
"The sympathies of the Jury have been strongly moved in behalf of Bernardo de Soto, on account of his generous, noble and self-sacrificing conduct in saving the lives of more than 70 human beings, constituting the passengers and crew of the ship Minerva; and they desire that his case should be presented to the merciful consideration of the Government."
Judge Story replied that the wish of the jury would certainly be complied with both by the Court and the prosecuting officer.
"The appearance and demeanor of Captain Gilbert are the same as when we first saw him; his eye is undimmed, and decision and command yet sit upon his features. We did not discern the slightest alteration of color or countenance when the verdict of the jury was communicated to him; he merely slightly bowed and resumed his seat. With De Soto the case was different. He is much altered; has become thinner, and his countenance this morning was expressive of the deepest despondency. When informed of the contents of the paper read by the foreman of the jury, he appeared much affected, and while being removed from the Court, covered his face with his handkerchief."
Immediately after the delivery of the verdict, the acquitted prisoners, on motion of Mr. Hillard, were directed to be discharged, upon which several of the others loudly and angrily expressed their dissatisfaction at the result of the trial. Castillo (a half-caste, with an extremely mild and pleasing countenance,) pointed towards heaven, and called upon the Almighty to bear witness that he was innocent; Ruiz uttered some words with great vehemence; and Garcia said "all were in the same ship; and it was strange that some should be permitted to escape while others were punished." Most of them on leaving the Court uttered some invective against "the picaro who had sworn their lives away."
On Costa, the cabin boy, (aged 16) being declared "Not Guilty" some degree of approbation was manifested by the audience, but instantly checked by the judge, who directed the officers to take into custody, every one expressing either assent or dissent. We certainly think the sympathy expressed in favor of Costa very ill placed, for although we have not deemed ourselves at liberty to mention the fact earlier, his conduct during the whole trial was characterized by the most reckless effrontery and indecorum. Even when standing up to receive the verdict of the jury, his face bore an impudent smile, and he evinced the most total disregard of the mercy which had been extended towards him.
About this time vague rumors reached Corunna, that a Captain belonging to that place, engaged in the Slave Trade, had turned Pirate, been captured, and sent to America with his crew for punishment. Report at first fixed it upon a noted slave-dealer, named Begaro. But the astounding intelligence soon reached Senora de Soto, that her husband was the person captured for this startling crime. The shock to her feelings was terrible, but her love and fortitude surmounted them all; and she determined to brave the terrors of the ocean, to intercede for her husband if condemned, and at all events behold him once more. A small schooner was freighted by her own and husband's father, and in it she embarked for New-York. After a boisterous passage, the vessel reached that port, when she learned her husband had already been tried and condemned to die. The humane people of New-York advised her to hasten on to Washington, and plead with the President for a pardon. On arriving at the capital, she solicited an interview with General Jackson, which was readily granted. From the circumstance of her husband's having saved the lives of seventy Americans, a merciful ear was turned to her solicitations, and a pardon for De Soto was given her, with which she hastened to Boston, and communicated to him the joyful intelligence.
Andrew Jackson, President of the United States of America, to all to whom these presents shall come, Greeting: Whereas, at the October Term, 1834, of the Circuit Court of the United States, Bernardo de Soto was convicted of Piracy, and sentenced to be hung on the 11th day of March last from which sentence a respite was granted him for three months, bearing date the third day of March, 1835, also a subsequent one, dated on the fifth day of June, 1835, for sixty days. And whereas the said Bernardo de Soto has been represented as a fit subject for executive clemency--
Now therefore, I, Andrew Jackson, President of the United States of America, in consideration of the premises, divers good and sufficient causes me thereto moving, have pardoned, and hereby do pardon the said Bernardo de Soto, from and after the 11th August next, and direct that he be then discharged from confinement. In testimony whereof I have hereunto subscribed my name, and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed to these presents. Done at the City of Washington the sixth day of July, AD. 1835, and of the independence of the United States and sixtieth. Andrew Jackson.
On the fatal morning of June 11th, 1835, Don Pedro, Juan Montenegro, Manuel Castillo, Angel Garcia and Manuel Boyga, were, agreeably to sentence, summoned to prepare for immediate execution. On the night previous, a mutual agreement had been entered into to commit suicide. Angel Garcia made the first attempt by trying to open the veins of each arm with a piece of glass; but was prevented. In the morning, however, while preparations were making for the execution, Boyga succeeded in inflicting a deep gash on the left side of his neck, with a piece of tin. The officer's eyes had been withdrawn from him scarcely a minute, before he was discovered lying on his pallet, with a convulsive motion of his knees, from loss of blood. Medical aid was at hand, the gash sewed up, but he did not revive. Two Catholic clergymen attended them on the scaffold, one a Spanish priest. They were executed in the rear of the jail. When the procession arrived at the foot of the ladder leading up to the platform of the gallows the Rev. Mr. Varella looking directly at Capt. Gilbert, said, "Spaniards, ascend to heaven." Don Pedro mounted with a quick step, and was followed by his comrades at a more moderate pace, but without the least hesitation. Boyga, unconscious of his situation and destiny, was carried up in a chair, and seated beneath the rope prepared for him. Gilbert, Montenegro, Garcia and Castillo all smiled subduedly as they took their stations on the platform. Soon after Capt. Gilbert ascended the scaffold, he passed over to where the apparently lifeless Boyga was seated in the chair, and kissed him. Addressing his followers, he said, "Boys, we are going to die; but let us be firm, for we are innocent." To Mr. Peyton, the interpreter, he said, "I die innocent, but I'll die like a noble Spaniard. Good bye, brother." The Marshal having read the warrant for their execution, and stated that de Soto was respited sixty and Ruiz thirty days, the ropes were adjusted round the necks of the prisoners, and a slight hectic flush spread over the countenance of each; but not an eye quailed, nor a limb trembled, not a muscle quivered. The fatal cord was now cut, and the platform fell, by which the prisoners were launched into eternity. After the execution was over, Ruiz, who was confined in his cell, attracted considerable attention, by his maniac shouts and singing. At one time holding up a piece of blanket, stained with Boyga's blood, he gave utterance to his ravings in a sort of recitative, the burden of which was--"This is the red flag my companions died under!"
After the expiration of Ruiz' second respite, the Marshal got two surgeons of the United States Navy, who understood the Spanish language, to attend him in his cell; they, after a patient examination pronounced his madness a counterfeit, and his insanity a hoax. Accordingly, on the morning of Sept. 11th, the Marshal, in company with a Catholic priest and interpreter entered his cell, and made him sensible that longer evasion of the sentence of the law was impossible, and that he must surely die. They informed him that he had but half an hour to live, and retired; when he requested that he might not be disturbed during the brief space that remained to him, and turning his back to the open entrance to his cell, he unrolled some fragments of printed prayers, and commenced reading them to himself. During this interval he neither spoke, nor heeded those who were watching him; but undoubtedly suffered extreme mental agony. At one minute he would drop his chin on his bosom, and stand motionless; at another would press his brow to the wall of his cell, or wave his body from side to side, as if wrung with unutterable anguish. Suddenly, he would throw himself upon his knees on the mattress, and prostrate himself as if in prayer; then throwing his prayers from him, he would clutch his rug in his fingers, and like a child try to double it up, or pick it to pieces. After snatching up his rug and throwing it away again and again, he would suddenly resume his prayers and erect posture, and stand mute, gazing through the aperture that admitted the light of day for upwards of a minute. This scene of imbecility and indecision, of horrible prostration of mind, ceasing in some degree when the Catholic clergyman re-entered his cell.
At 10 o'clock, the prisoner was removed from the prison, and during his progress to the scaffold, though the hue of death was on his face, and he trembled in every joint with fear, he chaunted with a powerful voice an appropriate service from the Catholic ritual. Several times he turned round to survey the heavens which at that moment were clear and bright above him and when he ascended the scaffold after concluding his prayer, he took one long and steadfast look at the sun, and waited in silence his fate. His powers, mental and physical had been suddenly crushed with the appalling reality that surrounded him; his whole soul was absorbed with one master feeling, the dread of a speedy and violent death. He quailed in the presence of the dreadful paraphernalia of his punishment, as much as if he had been a stranger to deeds of blood, and never dealt death to his fellow man as he ploughed the deep, under the black flag of piracy, with the motto of "Rob, Kill, and Burn." After adjusting the rope, a signal was given. The body dropped heavily, and the harsh abrupt shock must have instantly deprived him of sensation, as there was no voluntary action of the hands afterwards. Thus terminated his career of crime in a foreign land without one friend to recognize or cheer him, or a single being to regret his death.
The Spanish Consul having requested that the bodies might not
be given to the faculty, they were interred at night under the
direction of the Marshal, in the Catholic burial-ground at
Charlestown. There being no murder committed with the piracy, the
laws of the United States do not authorize the court to order the
bodies for dissection.
