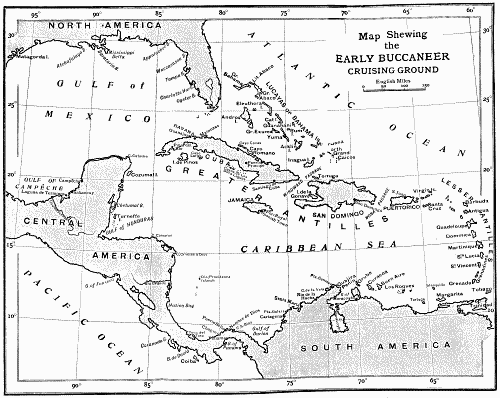
On the Spanish Main, by John Masefield
CHAPTER XX
IN ACTION
In engaging an enemy's ship at sea the custom was to display the colours from the poop, and to hang streamers or pennons from the yardarms.[30] The spritsail would then be furled, and the spritsail-yard brought alongship. The lower yards were slung with chain, and the important ropes, sheets and braces,[31] etc., were doubled. The bulkheads and wooden cabin walls were knocked away, or fortified with hammocks or bedding, to minimise the risk of splinters. The guns were cast loose and loaded. The powder or cartridge was brought up in "budge barrels," covered with leather, from the magazine, and stowed well away from the guns, either in amidships, or on that side of the ship not directly engaged. Tubs of water were placed between the guns with blankets soaking in them for the smothering of any fire that might be caused. Other tubs were filled with "vinegar water or what we have" for the sponging of the guns. The hatches leading to the hold were taken up, so that no man should desert his post during the engagement. The light sails were furled, and in some cases sent down on deck. The magazines were opened, and hung about with wet blankets to prevent sparks from entering. Shot was sent to the shot-lockers on deck. Sand was sprinkled on the planking to give a greater firmness to the foothold of the men at the guns. The gunner and his mates went round the batteries to make sure that all was ready. The caps, or leaden plates,[335] were taken from the touch-holes, and the priming powder was poured down upon the cartridge within the gun. The carpenter made ready sheets of lead, and plugs of oakum, for the stopping of shot-holes.[32] The cook-room fire was extinguished. The sails were splashed with a solution of alum. The people went to eat and drink at their quarters. Extra tiller ropes, of raw hide, were rove abaft. The trumpeters put on their[33] tabards, "of the Admiral's colours," and blew points of war as they sailed into action. A writer of the early seventeenth century[34] has left the following spirited account of a sea-fight:—
"A sail, how bears she or stands shee, to winde-ward or lee-ward? set him by the Compasse; he stands right ahead, or on the weather-Bowe, or lee-Bowe, let fly your colours if you have a consort, else not. Out with all your sails, a steady man to the helme, sit close to keep her steady, give him chase or fetch him up; he holds his own, no, we gather on him. Captain, out goes his flag and pendants, also his waste-clothes and top-armings, which is a long red cloth about three quarters of a yard broad, edged on each side with Calico, or white linnen cloth, that goeth round about the ship on the outsides of all her upper works fore and aft, and before the cubbridge-heads, also about the fore and maine tops, as well for the countenance and grace of the ship, as to cover the men for being seen, he furies and slinges his maine yarde, in goes his spret-saile. Thus they use to strip themselves into their short sailes, or fighting sailes, which is only the fore sail, the main and fore topsails, because the rest should not be fired nor spoiled; besides they would be troublesome to handle, hinder our fights and the using our armes; he makes ready his close fights fore and aft.
"Master, how stands the chase? Right on head I say;[336] Well we shall reatch him by and by; what's all ready? Yea, yea, every man to his charge, dowse your topsaile to salute him for the Sea, hale him with a noise of trumpets; Whence is your ship? Of Spaine; Whence is yours? Of England. Are you a Merchant, or a Man of War? We are of the Sea. He waves us to Lee-ward with his drawne Sword, cals amaine for the King of Spaine and springs his loufe. Give him a chase piece with your broadside, and run a good berth ahead of him; Done, done. We have the winde of him, and he tackes about, tacke you aboute also and keep your loufe [keep close to the wind] be yare at the helme, edge in with him, give him a volley of small shot, also your prow and broadside as before, and keep your loufe; He payes us shot for shot; Well, we shall requite him; What, are you ready again? Yea, yea. Try him once more, as before; Done, Done; Keep your loufe and charge your ordnance again; Is all ready? Yea, yea, edge in with him again, begin with your bowe pieces, proceed with your broadside, and let her fall off with the winde, to give her also your full chase, your weather broadside, and bring her round that the stern may also discharge, and your tackes close aboord again; Done, done, the wind veeres, the Sea goes too high to boord her, and we are shot thorow and thorow, and betwene winde and water. Try the pump, bear up the helme; Master let us breathe and refresh a little, and sling a man overboard [i.e. lower a man over the side] to stop the leakes; that is, to trusse him up aboute the middle in a piece of canvas, and a rope to keep him from sinking, and his armes at liberty, with a malet in the one hand, and a plug lapped in Okum, and well tarred in a tarpawling clowt in the other, which he will quickly beat into the hole or holes the bullets made; What cheere mates? is all well? All well, all well, all well. Then make ready to bear up with him again, and with all your[337] great and small shot charge him, and in the smoke boord him thwart the hawse, on the bowe, midships, or rather than faile, on the quarter [where the high poop made it difficult to climb on board] or make fast your graplings [iron hooks] if you can to his close fights and shear off [so as to tear them to pieces]. Captain, we are fowl on each other, and the Ship is on fire, cut anything to get clear and smother the fire with wet clothes. In such a case they will presently be such friends, as to helpe one the other all they can to get clear, lest they should both burn together and sink; and if they be generous, the fire quenched, drink kindely one to another; heave their cans overboord, and then begin again as before.
"Well, Master, the day is spent, the night drawes on, let us consult. Chirurgion, look to the wounded, and winde up the slain, with each a weight or bullet at their heades and feet to make them sinke, and give them three Gunnes for their funerals. Swabber, make clean the ship [sprinkle it with hot vinegar to avoid the smell of blood]; Purser, record their Names; Watch, be vigilant to keep your berth to windeward that we lose him not in the night; Gunners, spunge your Ordnance; Sowldiers, scowre your pieces; Carpenters about your leakes; Boatswaine and the rest repair your sails and shrouds; and Cooke, you observe your directions against the morning watch; Boy, Holla, Master, Holla, is the Kettle boiled? Yea, yea; Boatswaine, call up the men to prayer and breakfast [We may suppose the dawn has broken].
"Boy, fetch my cellar of bottels [case of spirits], a health to you all fore and aft, courage my hearts for a fresh charge; Gunners beat open the ports, and out with your lower tire [lower tier of guns] and bring me from the weather side to the lee, so many pieces as we have ports to bear upon him. Master lay him aboord loufe for loufe; mid Ships men, see the tops and yards well manned, with[338] stones, fire pots and brass bailes, to throw amongst them before we enter, or if we be put off, charge them with all your great and small shot, in the smoke let us enter them in the shrouds, and every squadron at his best advantage; so sound Drums and Trumpets, and Saint George for England.
"They hang out a flag of truce, hale him a main, abase, or take in his flag [to hale one to amaine, a main or a-mayn, was to bid him surrender; to abase was to lower the colours or the topsails], strike their sails, and come aboord with their Captaine, Purser, and Gunner, with their commission, cocket, or bills of loading. Out goes the boat, they are launched from the ship's side, entertaine them with a generall cry God save the Captain and all the company with the Trumpets sounding, examine them in particular, and then conclude your conditions, with feasting, freedom or punishment as you find occasion; but alwayes have as much care to their wounded as your own, and if there be either young women or aged men, use them nobly, which is ever the nature of a generous disposition. To conclude, if you surprise him, or enter perforce, you may stow the men, rifle, pillage, or sack, and cry a prise."
Down below in the gun-decks during an action, the batteries became so full of the smoke of black powder that the men could hardly see what they were doing. The darkness prevented them from seeing the very dangerous recoiling of the guns, and many were killed by them. It was impossible to judge how a gun carriage would recoil, for it never recoiled twice in the same manner, and though the men at the side tackles did their best to reduce the shock they could not prevent it altogether. It was the custom to close the gun-ports after each discharge, as the musketeers aboard the enemy could otherwise fire through them as the men reloaded. The[339] guns were not fired in a volley, as no ship could have stood the tremendous shock occasioned by the simultaneous discharge of all her guns. They were fired in succession, beginning from the bows. In heavy weather the lower tiers of guns were not cast loose, for the rolling made them difficult to control, and the sea came washing through the ports and into the muzzles of the guns, knocking down the men and drenching the powder. It sometimes happened that the shot, and cartridge, were rolled clean out of the guns. In sponging and ramming the men were bidden to keep the sponge or rammer on that side of them opposite to the side exposed to the enemy so that if a shot should strike it, it would not force it into the body of the holder. A man was told off to bring cartridges and shot to each gun or division of guns and he was strictly forbidden to supply any other gun or guns during the action. The wounded were to be helped below by men told off especially for the purpose. Once below, in the cockpit, they were laid on a sail, and the doctor or his mates attended to them in turn. In no case was a man attended out of his turn. This system seems equitable, and the sailors were insistent that it should be observed; but many poor fellows bled to death, from shattered arteries, etc., while waiting till the doctor should be ready. The chaplain attended in the cockpit to comfort the dying, and administer the rites of the Church. When a vessel was taken, her crew were stripped by those in want of clothes. The prisoners were handcuffed, or chained together, and placed in the hold, on the ballast. The ship's company then set to work to repair damages, clean and secure the guns, return powder, etc., to the armoury, and magazines, and to give thanks for their preservation round the main-mast.
[30] Monson.
[31] Ibid.
[32] Monson.
[33] Ibid.
[34] Captain John Smith.