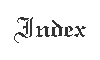Negro idols found in Mexico
1. Lenormant insists that the human race issued from Ups Merou, and adds that some Greek traditions point to "this locality--particularly the expression me'ropes a?'nðwpoi, which can only mean 'the men sprung from Merou.'" ("Manual," p.21.)
Theopompus tells us that the people who inhabited Atlantis were the Meropes, the people of Merou.
2. Whence comes the word Atlantic? The dictionaries tell us that the ocean is named after the mountains of Atlas; but whence did the Atlas mountains get their name?
"The words Atlas and Atlantic have no satisfactory etymology in any language known to Europe. They are not Greek, and cannot be referred to any known language of the Old World. But in the Nahuatl language we find immediately the radical a, atl, which signifies water, war, and the top of the head. (Molina, "Vocab. en lengua Mexicana y Castellana.") From this comes a series of words, such as atlan--on the border of or amid the water--from which we 'have the adjective Atlantic. We have also atlaça, to combat, or be in agony; it means likewise to hurl or dart from the water, and in the preterit makes Atlaz. A city named Atlan existed when the continent was discovered by Columbus, at the entrance of the Gulf of Uraba, in Darien. With a good harbor, it is now reduced to an unimportant pueblo named Acla." (Baldwin's "Ancient America," p. 179.)
Plato tells us that Atlantis and the Atlantic Ocean were named after Atlas, the eldest son of Poseidon, the founder of the kingdom.
3. Upon that part of the African continent nearest to the site of Atlantis we find a chain of mountains, known from the most ancient times as the Atlas Mountains. Whence this name Atlas, if it be not from the name of the great king of Atlantis? And if this be not its origin, how comes it that we find it in the most north-western corner of Africa? And how does it happen that in the time of Herodotus there dwelt near this mountain-chain a people called the Atlantes, probably a remnant of a colony from Solon's island? How comes it that the people of the Barbary States were known to the Greeks, Romans, and Carthaginians as the "Atlantes," this name being especially applied to the inhabitants of Fezzan and Bilma? Where did they get the name from? There is no etymology for it east of the Atlantic Ocean. (Lenormants "Anc. Hist. of the East," p. 253.)
Look at it! An "Atlas" mountain on the shore of Africa; an "Atlan" town on the shore of America; the "Atlantes" living along the north and west coast of Africa; an Aztec people from Aztlan, in Central America; an ocean rolling between the two worlds called the "Atlantic;" a mythological deity called "Atlas" holding the world on his shoulders; and an immemorial tradition of an island of Atlantis. Can all these things be the result of accident?
4. Plato says that there was a "passage west from Atlantis to the rest of the islands, as well as from these islands to the whole opposite continent that surrounds that real sea." He calls it a real sea, as contradistinguished from the Mediterranean, which, as he says, is not a real sea (or ocean) but a landlocked body of water, like a harbor.
Now, Plato might have created Atlantis out of his imagination; but how could he have invented the islands beyond (the West India Islands), and the whole continent (America) enclosing that real sea? If we look at the map, we see that the continent of America does "surround" the ocean in a great half-circle. Could Plato have guessed all this? If there had been no Atlantis, and no series of voyages from it that revealed the half-circle of the continent from Newfoundland to Cape St. Roche, how could Plato have guessed it? And how could he have known that the Mediterranean was only a harbor compared with the magnitude of the great ocean surrounding Atlantis? Long sea-voyages were necessary to establish that fact, and the Greeks, who kept close to the shores in their short journeys, did not make such voyages.
5. How can we, without Atlantis, explain the presence of the Basques in Europe, who have no lingual affinities with any other race on the continent of Europe, but whose language is similar to the languages of America?
Plato tells us that the dominion of Gadeirus, one of the kings of Atlantis, extended "toward the pillars of Heracles (Hercules) as far as the country which is still called the region of Gades in that part of the world." Gades is the Cadiz of today, and the dominion of Gadeirus embraced the land of the Iberians or Basques, their chief city taking its name from a king of Atlantis, and they themselves being Atlanteans.
Dr. Farrar, referring to the Basque language, says:
"What is certain about it is, that its structure is polysynthetic, like the languages of America. Like them, it forms its compounds by the elimination of certain radicals in the simple words; so that ilhun, the twilight, is contracted from hill, dead, and egun, day; and belhaur, the knee, from belhar, front, and oin, leg. . . . The fact is indisputable, and is eminently noteworthy, that while the affinities of the Basque roots have never been conclusively elucidated, there has never been any doubt that this isolated language, preserving its identity in a western corner of Europe, between two mighty kingdoms, resembles, in its grammatical structure, the aboriginal languages of the vast opposite continent (America), and those alone." ("Families of Speech," p. 132.)

Negro idols found in Mexico
If there was an Atlantis, forming, with its connecting ridges, a continuous bridge of land from America to Africa, we can understand how the Basques could have passed from one continent to another; but if the wide Atlantic rolled at all times unbroken between the two continents, it is difficult to conceive of such an emigration by an uncivilized people.
6. Without Atlantis, how can we explain the fact that the early Egyptians were depicted by themselves as red men on their own monuments? And, on the other hand, how can we account for the representations of negroes on the monuments of Central America?
Dêsirè Charnay, now engaged in exploring those monuments, has published in the North American Review for December, 1880, photographs of a number of idols exhumed at San Juan de Teotihuacan, from which I select the following strikingly negroid faces:
Dr. Le Plongeon says:
"Besides the sculptures of long-bearded men seen by the explorer at Chichen Itza, there were tall figures of people with small heads, thick lips, and curly short hair or wool, regarded as negroes. 'We always see them as standard or parasol bearers, but never engaged in actual warfare.'" ("Maya Archæology," p. 62.)
 The following cut is from the court of the Palace of Palenque,
figured by Stephens. The face is strongly Ethiopian.
The following cut is from the court of the Palace of Palenque,
figured by Stephens. The face is strongly Ethiopian.
The figure below represents a gigantic granite head, found near the volcano of Tuxtla, in the Mexican State of Vera Cruz, at Caxapa. The features are unmistakably negroid.
As the negroes have never been a sea-going race, the presence of these faces among the antiquities of Central America proves one of two things, either the existence of a land connection between America and Africa via Atlantis, as revealed by the deep-sea soundings of the Challenger, or commercial relations between America and Africa through the ships of the Atlanteans or some other civilized race, whereby the negroes were brought to America as slaves at a very remote epoch.
And we find some corroboration of the latter theory in that singular book of the Quiches, the "Popol Vuh," in which, after describing the creation of the first men "in the region of the rising sun" (Bancroft's "Native Races," vol. v., p. 548), and enumerating their first generations, we are told, "All seem to have spoken one language, and to have lived in great peace, black men and white together. Here they awaited the rising of the sun, and prayed to the Heart of Heaven." (Bancroft's "Native Races," p. 547.) How did the red men of Central America know anything about "black men and white men?" The conclusion seems inevitable that these legends of a primitive, peaceful, and happy land, an Aztlan in the East, inhabited by black and white men, to which all the civilized nations of America traced their origin, could only refer to Atlantis--that bridge of land where the white, dark, and red races met. The "Popol Vuh" proceeds to tell how this first home of the race became over-populous, and how the people under Balam-Quitze migrated; how their language became "confounded," in other words, broken up into dialects, in consequence of separation; and how some of the people "went to the East, and many came hither to Guatemala." (Ibid., p. 547.)
M. A. de Quatrefages ("Human Species," p. 200) says, "Black populations have been found in America in very small numbers only, as isolated tribes in the midst of very different populations. Such are the Charruas, of Brazil, the Black Carribees of Saint Vincent, in the Gulf of Mexico; the Jamassi of Florida, and the dark-complexioned Californians. . . . Such, again, is the tribe that Balboa saw some representatives of in his passage of the Isthmus of Darien in 1513; . . . they were true negroes."

Negro head, Vera Cruz
7. How comes it that all the civilizations of the Old World
radiate from the shores of the Mediterranean? The Mediterranean
is a cul de sac, with Atlantis opposite its mouth. Every
civilization on its shores possesses traditions that point to
Atlantis. We hear of no civilization coining to the
Mediterranean from Asia, Africa, or Europe--from north, south, or
west; but north, south, east, and west we find civilization
radiating from the Mediterranean to other lands. We see the
Aryans descending upon Hindostan from the direction of the
Mediterranean; and we find the Chinese borrowing inventions from
Hindostan, and claiming descent from a region not far from the
Mediterranean.
The Mediterranean has been the centre of the modern world, because it lay in the path of the extension of an older civilization, whose ships colonized its shores, as they did also the shores .of America. Plato says, "the nations are gathered around the shores of the Mediterranean like frogs around a marsh."
Dr. McCausland says:
"The obvious conclusion from these facts is, that at some time previous to these migrations a people speaking a language of a superior and complicated structure broke up their society, and, under some strong impulse, poured out in different directions, and gradually established themselves in all the lands now inhabited by the Caucasian race. Their territories extend from the Atlantic to the Ganges, and from Iceland to Ceylon, and are bordered on the north and east by the Asiatic Mongols, and on the south by the negro tribes of Central Africa. They present all the appearances of a later race, expanding itself between and into the territories of two pre-existing neighboring races, and forcibly appropriating the room required for its increasing population." (McCausland's "Adam and the Adamites," p. 280.)
Modern civilization is Atlantean. Without the thousands of years of development which were had in Atlantis modern civilization could not have existed. The inventive faculty of the present age is taking up the great delegated work of creation where Atlantis left it thousands of years ago.
8. How are we to explain the existence of the Semitic race in Europe without Atlantis? It is an intrusive race; a race colonized on sea-coasts. Where are its Old World affinities?
9. Why is it that the origin of wheat, barley, oats, maize, and rye--the essential plants of civilization--is totally lost in the mists of a vast antiquity? We have in the Greek mythology legends of the introduction of most of these by Atlantean kings or gods into Europe; but no European nation claims to have discovered or developed them, and it has been impossible to trace them to their wild originals. Out of the whole flora of the world mankind in the last seven thousand years has not developed a single food-plant to compare in importance to the human family with these. If a wise and scientific nation should propose nowadays to add to this list, it would have to form great botanical gardens, and, by systematic and long-continued experiments, develop useful plants from the humble productions of the field and forest. Was this done in the past on the island of Atlantis?
10. Why is it that we find in Ptolemy's "Geography of Asia Minor," in a list of cities in Armenia Major in A.D. 140, the names of five cities which have their counterparts in the names of localities in Central America?
|
Armenian Cities. |
Central American Localities. |
|
Chol. |
Chol-ula |
|
Colua. |
Colua-can. |
|
Zuivana. |
Zuivan. |
|
Cholima. |
Colima. |
|
Zalissa. |
Xalisco. |
(Short's "North Americans of Antiquity," p. 497.)
11. How comes it that the sandals upon the feet of the statue of Chacmol, discovered at Chichen Itza, are "exact representations of those found on the feet of the Guanches, the early inhabitants of the Canary Islands, whose mummies are occasionally discovered in the eaves of Teneriffe?" Dr. Merritt deems the axe or chisel heads dug up at Chiriqui, Central America, "almost identical in form as well as material with specimens found in Suffolk County, England." (Bancroft's Native Races," vol. iv., p. 20.) The rock-carvings of Chiriqui are pronounced by Mr. Seemann to have a striking resemblance to the ancient incised characters found on the rocks of Northumberland, England. (Ibid.)
"Some stones have recently been discovered in Hierro and Las Palmas (Canary Islands), bearing sculptured symbols similar to those found on the shores of Lake Superior; and this has led M. Bertholet, the historiographer of the Canary Islands, to conclude that the first inhabitants of the Canaries and those of the great West were one in race." (Benjamin, "The Atlantic Islands," p. 130.)
12. How comes it that that very high authority, Professor Retzius ("Smithsonian Report," 1859, p. 266), declares, "With regard to the primitive dolichocephalæ of America I entertain a hypothesis still more bold, namely, that they are nearly related to the Guanches in the Canary Islands, and to the Atlantic populations of Africa, the Moors, Tuaricks, Copts, etc., which Latham comprises under the name of Egyptian-Atlantidæ. We find one and the same form of skull in the Canary Islands, in front of the African coast, and in the Carib Islands, on the opposite coast, which faces Africa. The color of the skin on both sides of the Atlantic is represented in these populations as being of a reddish-brown."
13. The Barbarians who are alluded to by Homer and Thucydides were a race of ancient navigators and pirates called Cares, or Carians, who occupied the isles of Greece before the Pelasgi, and antedated the Phœnicians in the control of the sea. The Abbé Brasseur de Bourbourg claims that these Carians were identical with the Caribs of the West Indies, the Caras of Honduras, and the Gurani of South America. (Landa's "Relacion," pp. 52-65.)
14. When we consider it closely, one of the most extraordinary customs ever known to mankind is that to which I have already alluded in a preceding chapter, to wit, the embalming of the body of the dead man, with a purpose that the body itself may live again in a future state. To arrive at this practice several things must coexist:
a. The people must be highly religious, and possessed of an organized and influential priesthood, to perpetuate so troublesome a custom from age to age.
b. They must believe implicitly in the immortality of the soul; and this implies a belief in rewards and punishments after death; in a heaven and a hell.
c. They must believe in the immortality of the body, and its resurrection from the grave on some day of judgment in the distant future.
d. But a belief in the immortality of the soul and the resurrection of the body is not enough, for all Christian nations hold to these beliefs; they must supplement these with a determination that the body shall not perish; that the very flesh and blood in which the man died shall rise with him on the last day, and not a merely spiritual body.
Now all these four things must coexist before a people proceed to embalm their dead for religious purposes. The probability that all these four things should coexist by accident in several widely separated races is slight indeed. The doctrine of chances is all against it. There is here no common necessity driving men to the same expedient, with which so many resemblances have been explained; the practice is a religious ceremony, growing out of religious beliefs by no means common or universal, to wit, that the man who is dead shall live again, and live again in the very body in which he died. Not even all the Jews believed in these things.
If, then, it should appear that among the races which we claim were descended from Atlantis this practice of embalming the dead is found, and nowhere else, we have certainly furnished evidence which can only be explained by admitting the existence of Atlantis, and of some great religious race dwelling on Atlantis, who believed in the immortality of soul and body, and who embalmed their dead. We find, as I have shown:
First. That the Guanches of the Canary Islands, supposed to be a remnant of the Atlantean population, preserved their dead as mummies.
Second. That the Egyptians, the oldest colony of Atlantis, embalmed their dead in such vast multitudes that they are now exported by the ton to England, and ground up into manures to grow English turnips.
Third. That the Assyrians, the Ethiopians, the Persians, the Greeks, and even the Romans embalmed their dead.
Fourth. On the American continents we find that the Peruvians, the Central Americans, the Mexicans, and some of the Indian tribes, followed the same practice.
Is it possible to account for this singular custom, reaching through a belt of nations, and completely around the habitable world, without Atlantis?
15. All the traditions of the Mediterranean races look to the ocean as the source of men and gods. Homer sings of
"Ocean, the origin of gods and Mother Tethys."
Orpheus says, "The fair river of Ocean was the first to marry, and he espoused his sister Tethys, who was his mothers daughter." (Plato's "Dialogues," Cratylus, p. 402.) The ancients always alluded to the ocean as a river encircling the earth, as in the map of Cosmos (see page 95 ante); probably a reminiscence of the great canal described by Plato which surrounded the plain of Atlantis. Homer (Iliad, book xviii.) describes Tethys, "the mother goddess," coming to Achilles "from the deep abysses of the main:"
"The circling Nereids with their mistress weep,
And all the sea-green sisters of the deep."
Plato surrounds the great statue of Poseidon in Atlantis with the images of one hundred Nereids.
16. in the Deluge legends of the Hindoos (as given on page 87 ante), we have seen Manu saving a small fish, which subsequently grew to a great size, and warned him of the coming of the Flood. In this legend all the indications point to an ocean as the scene of the catastrophe. It says: "At the close of the last calpa there was a general destruction, caused by the sleep of Brahma, whence his creatures, in different worlds, were drowned in a vast ocean. . . . A holy king, named Satyavrata, then reigned, a servant of the spirit which moved on the waves" (Poseidon?), "and so devout that water was his only sustenance. . . . In seven days the three worlds" (remember Poseidon's trident) "shall be plunged in an ocean of death." . . . "'Thou shalt enter the spacious ark, and continue in it secure from the Flood on one immense ocean.' . . . The sea overwhelmed its shores, deluged the whole earth, augmented by showers from immense clouds." ("Asiatic Researches," vol. i., p. 230.)
All this reminds us of "the fountains of the great deep and the flood-gates of heaven," and seems to repeat precisely the story of Plato as to the sinking of Atlantis in the ocean.
17. While I do not attach much weight to verbal similarities in the languages of the two continents, nevertheless there are some that are very remarkable. We have seen the Pan and Maia of the Greeks reappearing in the Pan and Maya of the Mayas of Central America. The god of the Welsh triads, "Hu the mighty," is found in the Hu-nap-bu, the hero-god of the Quiches; in Hu-napu, a hero-god; and in Hu-hu-nap-hu, in Hu-ncam, in Hu-nbatz, semi-divine heroes of the Quiches. The Phœnician deity El "was subdivided into a number of hypostases called the Baalim, secondary divinities, emanating from the substance of the deity" ("Anc. Hist. East," vol. ii., p. 219); and this word Baalim we find appearing in the mythology of the Central Americans, applied to the semi-divine progenitors of the human race, Balam-Quitze, Balam-Agab, and Iqui-Balam.